




Next: Data functions
Up: [B/D] operands and operators
Previous: Accessing belief sources used
All arithmetic operators take one argument E in parenthesis, where E
is any valid equation.
-
abs returns the absolute value of the argument. For
example,
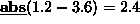 .
.
-
arctan is the hyperbolic tangent function, returning the
value whose tangent is the given argument. For example,
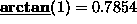 .
.
-
cos returns the cosine of its argument. For example,
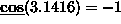
-
exp returns E to the power of its argument. For
example,
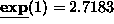
-
ln returns the natural logarithm of the argument E. A
non-positive argument causes an error. For example,
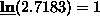
-
sgn returns one of three values according to the sign
of its argument: zero if the argument is zero;
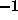 if the argument
is negative; and
if the argument
is negative; and 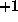 if the argument is positive. For example
if the argument is positive. For example
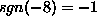 .
.
-
sin returns the sine of its argument. For example,
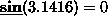 .
.
-
sqr returns the square of its argument. For example,
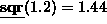 .
.
-
sqrt returns the square-root of its argument.
An error will be reported if the argument is negative. For example,
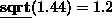 .
.
-
trunc returns the integer truncation of its argument. For
example,
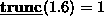 .
.
David Wooff
Wed Oct 21 15:14:31 BST 1998